
This economic arrangement was known as the manorial system. The deprivation of the leftovers of property caused a protest of the peasantry. It could be grain, flour, beer, wine, poultry, eggs or handicrafts. From around 1100 or so, towns started to get charters from a bishop, a great lord. In exchange, serfs were given protected land to grow crops to support their families. The way the peasants lived in the Middle Ages depended on the size of the dues paid to the feudal lord. A town could be, and often was, defined legally in the Middle Ages. The knights and lords were in charge of maintaining order, protection, and enforcing rules and laws on their estates or manors. The serfs provided the lords or knights with labor to produce food and other goods they needed to maintain their lifestyles. The land given to knights or lords came with peasant farmers, known as serfs.
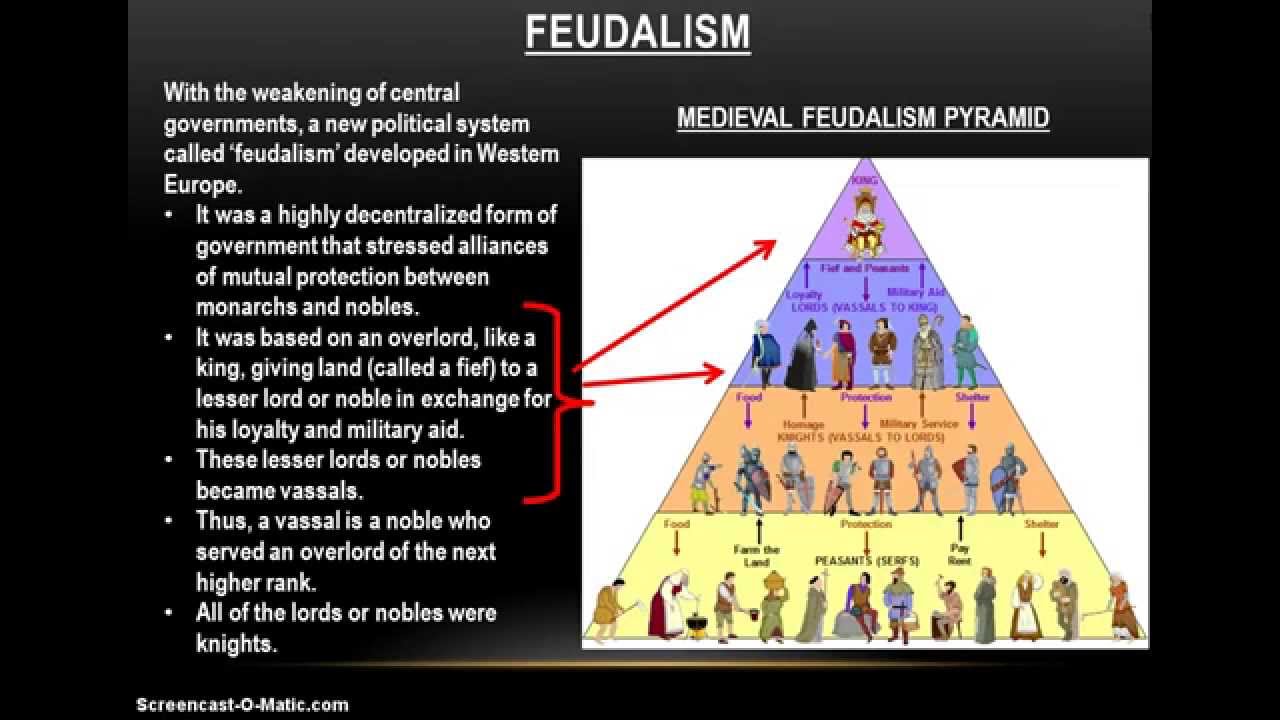
They agreed to 40 days of service each year in times of peace and more days in times of war. The kings offered land or estates, to warriors (also called knights or lords) in exchange for military service. Without a money system, collecting taxes was also tough. Before long, they began to depend on the nobles for food, horses. Paying for troops was impossible because society at this time lacked a money system. receive fiefs during the Middle Ages Reading Check. This allowed cooperation and security from lower classes in order to defend the upper class territory and maintain the work needed for national affairs.įeudalism was the medieval model of government. Therefore kings thought that if they invent a system that allows their citizens to have what they want with a substantial servitude to whoever grants them with their possessions, then they would be protected. There s nothing inherently wrong with hypotheses. This makes 'feudalism' a post-medieval concept. The term was first established in 16th-17th-century by intellectuals to define a political system of several hundred years earlier.

People of Western Europe needed protection from invading threats with control. The first thing we should recognize about the term feudalism is that it was never used during the Middle Ages. The social hierarchy included monarchs, nobles, knights, and peasants and serfs. They created a system of military and political relationships called feudalism. The system of feudalism began to flourish in the late 8th century, with Charlemagne being the most prominent early practitioner of the system.

To counter these threats, Frankish kings needed warriors. This resulted in a collapse of law and order, a decline in trade, and collapse of local economies. Beginning in the late 700s C.E., large numbers of invaders raided villages throughout Europe.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
